Engineering technology is a technical discipline that focuses on applications of developed technology. It is the middle ground between engineering and design realization. See more here: Introduction to Engineering Technology
The arrival of the space age signaled a need to advance the analytical depth of engineering education. As this analytical depth increased, many institutions found themselves cutting short much of the applied areas of engineering. Engineering technology was introduced to address the need for a technical workforce with a strong foundation in the basics of engineering, leaving the more complex analysis others.
Engineering technology is often described as a more “hands on” approach. Most engineering technology programs require a significant lab component.
References
“About – NICET.” NICET, https://www.nicet.org/about-us/. Accessed 2 Dec. 2022.
“Profession X | National Society of Professional Engineers.” National Society of Professional Engineers |, https://www.nspe.org/resources/pe-magazine/september-2017/profession-x. Accessed 2 Dec. 2022.
“The Origins of Engineering Technology Education | Engineering Technology Education in the United States |The National Academies Press.” The National Academies Press, https://nap.nationalacademies.org/read/23402/chapter/4. Accessed 2 Dec. 2022.
Wikimedia projects. “Engineering Technologist – Wikipedia.” Wikipedia, the Free Encyclopedia, Wikimedia Foundation, Inc., 22 Feb. 2004, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Engineering_technologist.
See Also
Machine Tools
Grinding and Abrasive Machining
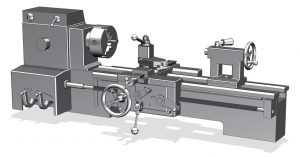
Lathes and Turning Operations
Drilling and Holemaking

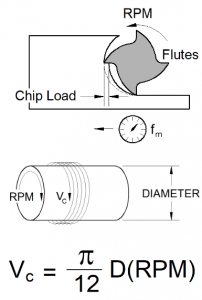
Machining Parameters
Sawing
Shapers and Planers


