Overmolding is a manufacturing process that involves the injection molding of one material over another to create a single, integrated component with multiple functional and aesthetic properties. The process typically involves molding a substrate or base material, which is then overmolded with a different material to achieve specific performance characteristics, such as improved grip, vibration dampening, or enhanced durability.
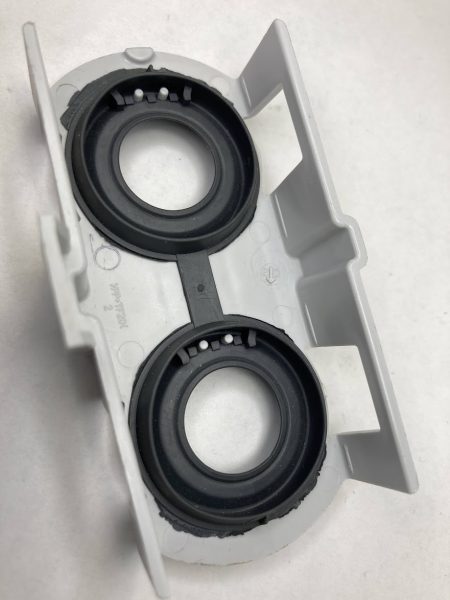

In overmolding, the base material is typically a rigid plastic or metal part, while the overmolded material is typically a soft, flexible, or elastomeric material that is injected over the base material. The two materials are bonded together during the molding process, creating a strong, seamless bond between the two components.
Overmolding can be used to create a wide range of products, from simple grips for handheld tools to complex medical devices with multiple functions. The process is commonly used in industries such as automotive, medical, consumer products, and electronics, where product performance, comfort, and aesthetics are critical.
One advantage of overmolding is that it can reduce the number of components needed in a product, which can simplify assembly and reduce overall manufacturing costs. Additionally, the use of different materials in the overmolding process can provide additional benefits such as improved ergonomics, increased durability, and improved aesthetics.
Overall, overmolding is a highly versatile and effective manufacturing process that allows for the creation of complex, integrated components with a range of performance and aesthetic properties. By leveraging the benefits of different materials, overmolding can provide manufacturers with the ability to produce highly functional and visually appealing products that meet the needs of today’s demanding markets.
