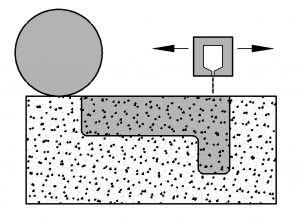
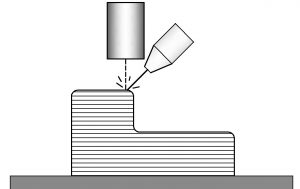
Additive manufacturing, often referred to as 3D printing, is a manufacturing process that builds three-dimensional objects layer by layer, directly from a digital design file. Unlike traditional subtractive manufacturing methods, which involve cutting, drilling, or shaping material to create a final product, additive manufacturing adds material in a sequential and precise manner. This process offers numerous advantages, including greater design flexibility, reduced waste, and the ability to produce complex geometries that are challenging or impossible to achieve with conventional techniques. Additive manufacturing has applications across various industries, from aerospace and automotive to healthcare and consumer goods, enabling rapid prototyping, customized production, and the potential for decentralized and on-demand manufacturing. It has the potential to transform how products are designed, produced, and distributed, leading to more efficient and innovative manufacturing processes in the future.

References
ASTM F2792-12a – Standard Terminology for Additive Manufacturing Technologies, (Withdrawn 2015)
his terminology includes terms, definitions of terms, descriptions of terms, nomenclature, and acronyms associated with additive-manufacturing (AM) technologies in an effort to standardize terminology used by AM users, producers, researchers, educators, press/media and others.
This standard references the following process categories:
- Binder Jetting
- Directed Energy Deposition
- Material Extrusion
- Material Jetting
- Powder Bed Fusion
- Sheet Lamination
- Vat Photopolymerization