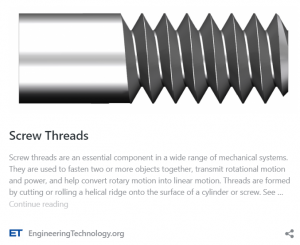
Threaded fasteners such as screws, bolts, and nuts, are essential mechanical components characterized by helical threads. These threads enable engagement with corresponding threads on another object, establishing a secure and often adjustable connection.
Screws are intended for insertion into materials using tools like screwdrivers or power tools. Bolts incorporate a flat or chamfered end and are used in conjunction with nuts to form a threaded connection. Nuts, generally hexagonal or square in shape, possess an internally threaded hole and are tightened onto bolt threads to secure two objects together.
Threaded fasteners offer notable advantages, including adjustability, facilitating easy disassembly and reassembly. Their helical threads ensure a robust and stable connection, resisting forces attempting to separate the components. Additionally, threaded fasteners are versatile, available in various sizes, lengths, and materials, making them suitable for diverse applications. Installation is straightforward, as screws and bolts can be easily affixed using manual tools or power tools.
The selection of threaded fasteners depends on factors such as the specific application, the materials involved, load requirements, and environmental conditions.
See also: Screw Threads