A draft angle is a slight angle added to the walls of a part in the manufacturing process to facilitate its removal from the mold or tooling.
In the manufacturing of molded parts, such as plastic parts or cast metal parts, a mold is used to form the part shape. The mold is usually made of two halves that come together to form the cavity in which the material is poured or injected. After the material has set and solidified, the mold halves must be separated to release the part.
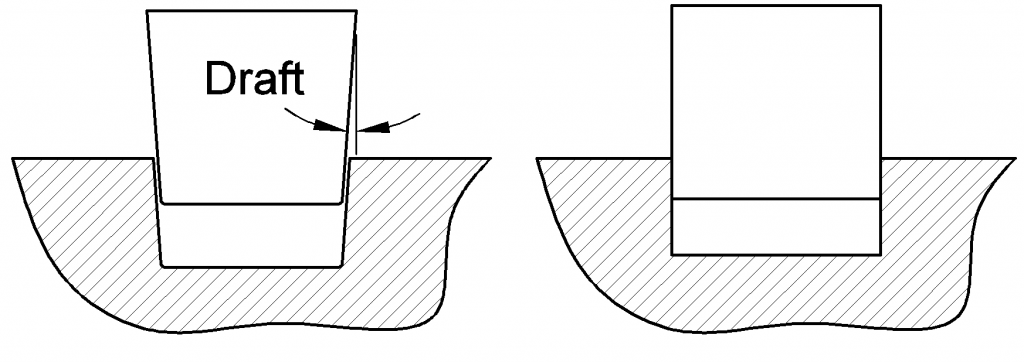
If the walls of the part are perpendicular to the mold surface, it can be difficult or impossible to separate the mold without damaging the part. This is where the draft angle comes in. By adding a slight angle to the walls of the part, it becomes easier to separate the mold and release the part. The angle allows the part to gradually “slide” out of the mold, reducing the risk of damage to the part or the mold.

The draft angle is typically measured in degrees and can vary depending on the material and molding process being used. For example, the draft angle for a plastic part may be different from the draft angle for a metal casting. The draft angle is an important feature in the design of parts for manufacturing, as it can greatly affect the ease and success of the manufacturing process.

