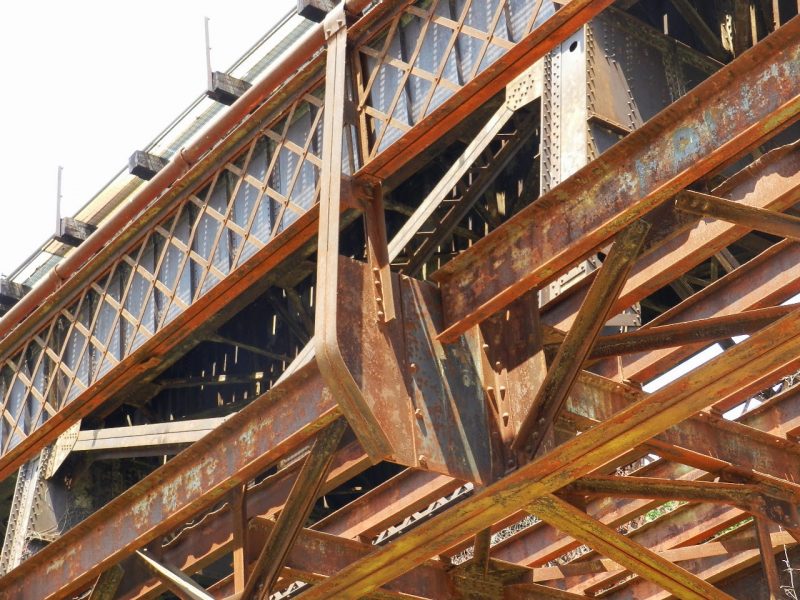
Steel is a widely used alloy of iron and carbon, with carbon content typically ranging from 0.2% to 2.1% by weight. It is known for its high strength, durability, and versatility, making it a popular choice in a wide range of applications, including construction, manufacturing, and transportation. Steel can be produced in a variety of...

Cast iron is a group of iron-carbon alloys with a carbon content greater than 2%. It is known for its excellent castability and unique properties, making it a valuable material in various industrial applications. Cast iron has several advantages, including good castability, wear resistance, and excellent thermal conductivity and vibration dampening. However, it can be...

Wrought iron is a nearly obsolete type of iron that has been worked by hammering, bending, and shaping while it is in a heated, malleable state. It is characterized by its fibrous appearance, which is a result of the distinctive grain structure formed during the forging process. Wrought iron has been used for centuries in...

Ferrous MetallurgyIron Carbon Phase Diagram Heat Treatment of Steel Scale Formation & Prevention Differential Surface Chemistry Processes Pack Carburizing Selective Surface Heating Processes Steelmaking Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) See: AIST Steel Wheel Reference Ferrous metallurgy is a foundational field within materials science and engineering, focused on the study and manipulation of iron-based alloys, primarily steel....
Steel is a widely used alloy of iron and carbon, with carbon content typically ranging from 0.2% to...
Stainless steel is a versatile material known for its corrosion resistance, high strength, and aesthetic...
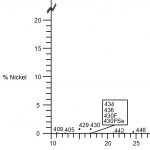
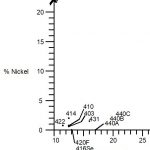
This group is the most common type of stainless steel and contains high levels of chromium (usually...
Ferritic stainless steels have little to no nickel. They are magnetic and offer good corrosion resistance,...
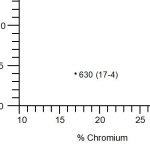
Martensitic stainless steels have a moderate chromium content (usually 12-18%) and low nickel. They...
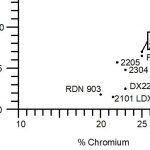
Duplex stainless steels combine the properties of both austenitic and ferritic stainless steels. They...
Precipitation-hardening stainless steels contain chromium, nickel, and other alloying elements such...
Tool steel is a type of high-quality carbon and alloy steel that is specifically designed for the production...
Types A2 through A10 are able to harden in an air quench.
Types A8 and A9 are low-carbon, and have...
Types H10 to H19 exhibit controlled chromium content alongside various other alloying elements. The...