Stainless steel is a versatile material known for its corrosion resistance, high strength, and aesthetic appeal. It is used in a wide range of applications, including construction, automotive, aerospace, medical, and food processing industries. In this article, we will explore the properties, types, and applications of stainless steel.
Properties of Stainless Steel

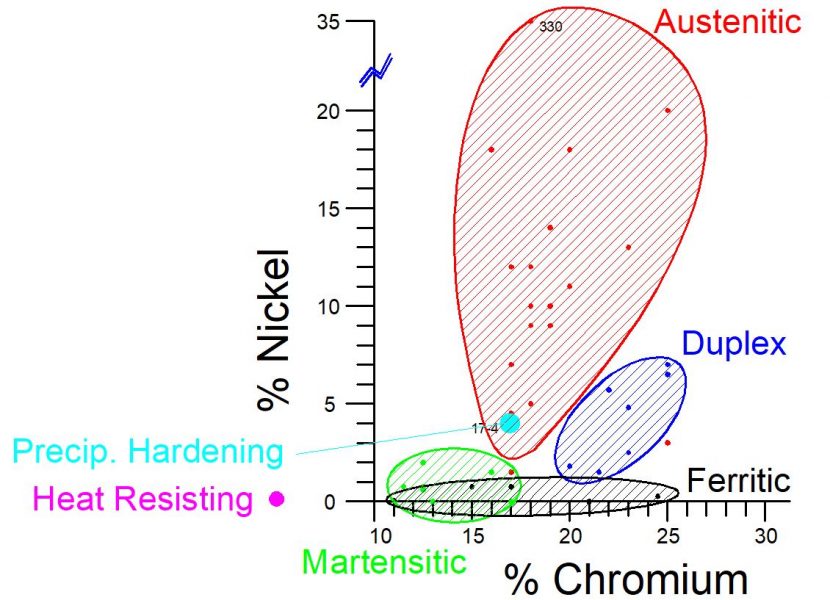
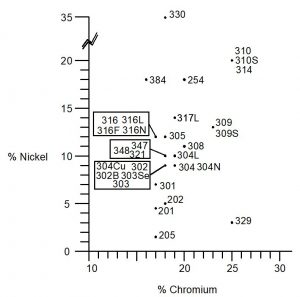
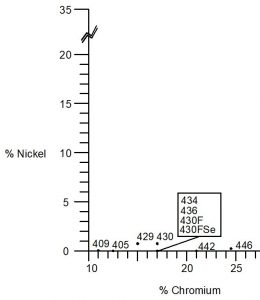
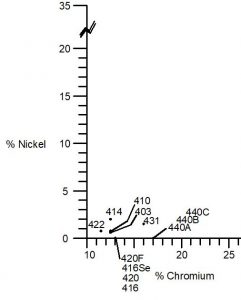
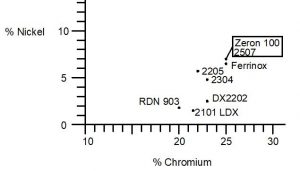
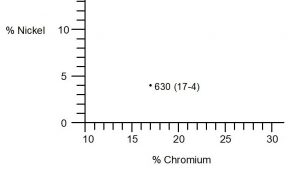
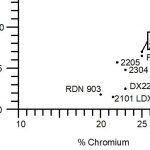
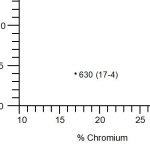
Stainless steel is an alloy of iron, carbon, and other elements such as chromium, nickel, and molybdenum. The addition of chromium gives stainless steel its unique properties, including resistance to corrosion and staining. The percentage of chromium in stainless steel varies, with the most common types containing between 10% and 20%.
Stainless steel is also known for its high strength, durability, and heat resistance. It is easy to clean and maintain, making it an ideal material for applications where hygiene is important, such as in the food and medical industries.