Textures are applied to certain surfaces to serve specific functional purposes, such as improving grip, reducing slippage, enhancing aesthetics, dampening noise, promoting adhesion, and facilitating lubrication in various applications and industries. References Decorating Techniques in Watchmaking
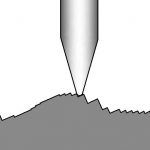
Surface texture refers to the characteristics of a material's outermost layer that can be observed and felt when touched or examined closely. It encompasses several key aspects, including surface roughness, waviness, and lay. Understanding and controlling surface texture is crucial for ensuring the desired performance, aesthetics, and functionality of products in fields ranging from manufacturing...

CoatingsOrganic Coatings Primers Drying Oils Varnish Spirit Varnish (Shellac) Lacquer Enamels Latex Paints Bituminous Coatings Synthetic Coating Resins Coating Methods Spray Coating Powder Coating Electrocoating (E-Coating) Inorganic Coatings Conversion Coatings Aluminum Anodizing Chromate Conversion Coatings Alodine Iridite Zinc Chromate Coatings Zinc Coatings Zinc Plating Dyes Coatings refer to thin layers of material applied to the...
Cleaning is a fundamental step that ensures surfaces are free from contaminants, residues, and impurities, making them suitable for subsequent manufacturing or finishing processes. This specific aspect of cleaning as surface preparation is crucial in various industries where the quality and performance of the final product depend on the cleanliness and condition of the surfaces...
https://engineeringtechnology.org/manufacturing/separating-processes/machining-processes/grinding-and-abrasive-machining/media-blasting/
Textures are applied to certain surfaces to serve specific functional purposes, such as improving grip,...
Half-moon flaking, also known as "half-moon scraping" and sometimes "frosting," is a scraping technique...
Laser texturing is a precision manufacturing technique that utilizes laser technology to modify the...
Surface texture refers to the characteristics of a material's outermost layer that can be observed and...
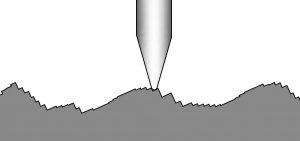
Lay refers to the predominant or primary direction of the surface texture pattern on a material or object....
Crossed lay (also known as intersecting, cross-hatched, or diagonal lay) is a specific orientation of...
Coatings refer to thin layers of material applied to the surface of a substrate or component...
Organic coatings refer to a category of protective and functional coatings primarily composed of...
Primers play a crucial role in the realm of coatings and painting, serving as preparatory layers that...
Drying oils are a class of vegetable oils that undergo a chemical transformation when exposed to air,...