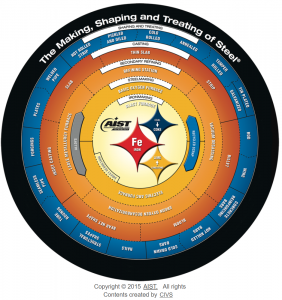
Steelmaking, also known as the steel production process or metallurgy, is the method of producing steel from iron ore and other raw materials. Steel is a versatile and widely used material in construction, manufacturing, and various industries due to its strength, durability, and flexibility.

The steelmaking process typically involves several key stages:
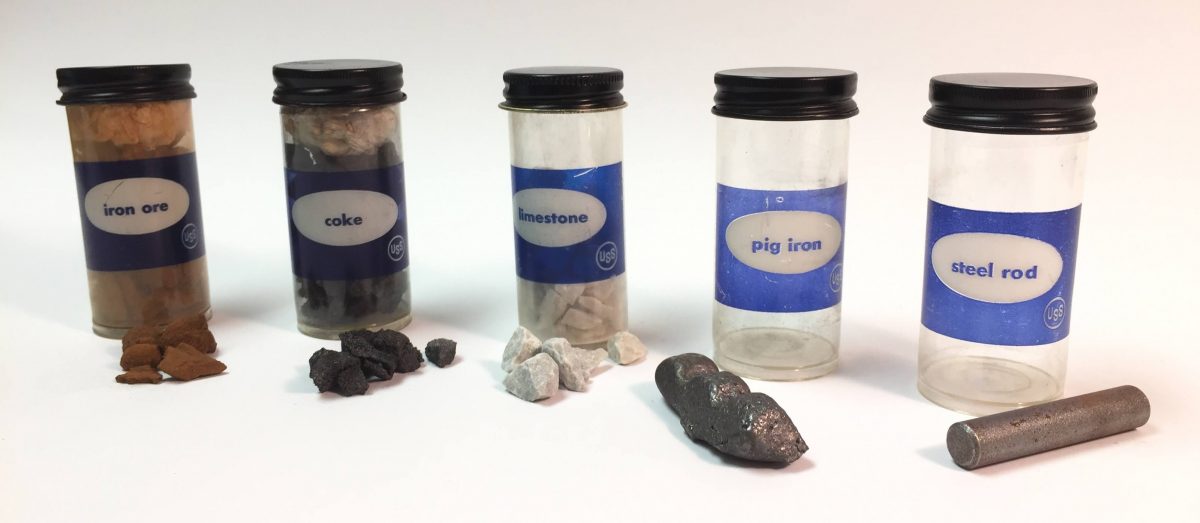
- Iron Ore Mining: The process begins with the extraction of iron ore from mines. Iron ore is a naturally occurring mineral that is rich in iron content.
- Iron Ore Processing: Once the iron ore is mined, it is often crushed and refined to remove impurities. This results in a more concentrated iron ore called iron ore concentrate or iron ore pellets.
- Iron Ore Reduction: Iron ore is then subjected to a process called reduction, where it is heated in a blast furnace with coke (a form of carbon) and limestone. This process removes oxygen from the iron ore, resulting in molten iron and slag (a byproduct).
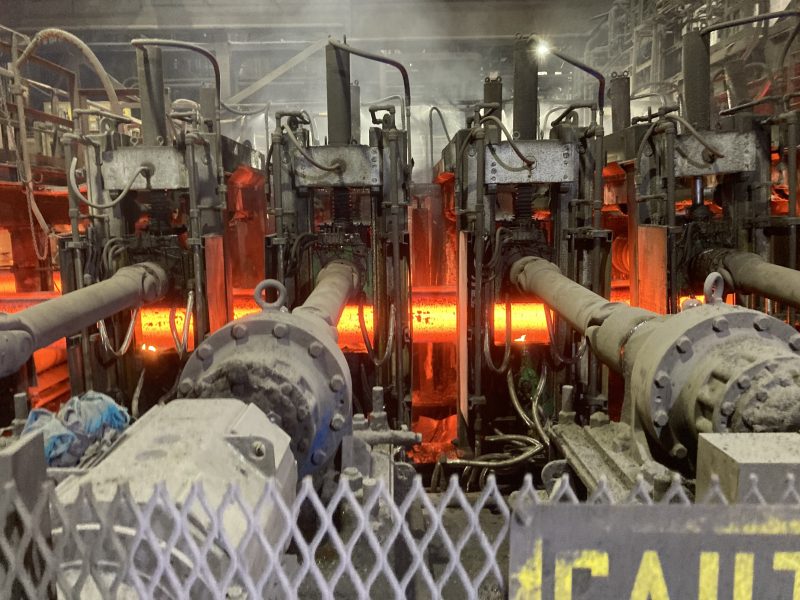
- Basic Oxygen Furnace (BOF) or Electric Arc Furnace (EAF): The molten iron from the blast furnace is either refined in a Basic Oxygen Furnace (BOF) or an Electric Arc Furnace (EAF). In the BOF, oxygen is blown into the molten iron to remove impurities, while in the EAF, electric arcs are used to melt scrap steel and adjust the composition as needed.
- Secondary Refining: In some cases, additional refining steps are performed to further improve the quality and properties of the steel. This may involve processes like ladle refining or vacuum degassing.
- Casting: After the steel is refined to the desired composition and quality, it is cast into various shapes, such as slabs, billets, or ingots, depending on the intended use.
- Forming and Finishing: The cast steel is then further processed and formed into specific products or shapes through rolling, forging, extrusion, or other methods. This step can vary widely depending on the intended application of the steel.
- Heat Treatment: Some steel products may undergo heat treatment processes like annealing, quenching, or tempering to enhance their mechanical properties.
- Quality Control: Throughout the steelmaking process, quality control measures are taken to ensure that the steel meets the required specifications and standards.

The choice of steelmaking process (BOF or EAF) and the specific steps involved can vary depending on factors such as the type of steel being produced, the desired properties, and economic considerations. Steelmaking is a critical industry that plays a crucial role in the construction of buildings, infrastructure, vehicles, machinery, and countless other products essential to modern society.