Hot chamber and cold chamber die casting machines are two of the most common types of die casting machines used in manufacturing. Both types of machines are used to produce high-precision metal parts through the die casting process, but they differ in how the molten metal is introduced into the mold.
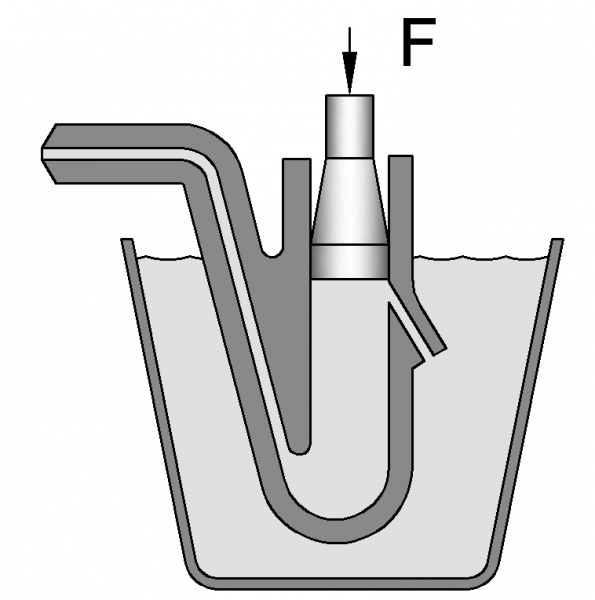
In hot chamber die casting machines, the metal to be cast is melted in a separate chamber and then transferred into the mold using a piston. This type of machine is typically used for casting low-melting point metals such as zinc and magnesium, as these metals can be easily melted and transferred into the mold without solidifying. The main advantage of hot chamber die casting is that it is a fast and efficient process, as the molten metal can be transferred into the mold quickly and repeatedly.
In contrast, cold chamber die casting machines have a separate chamber for melting the metal, which is then transferred into the casting machine using a ladle. This type of machine is typically used for casting high-melting point metals such as aluminum and copper alloys, as these metals cannot be melted and transferred into the mold as quickly as low-melting point metals. The main advantage of cold chamber die casting is that it allows for greater control over the casting process, as the temperature of the molten metal can be precisely regulated before it is introduced into the mold.
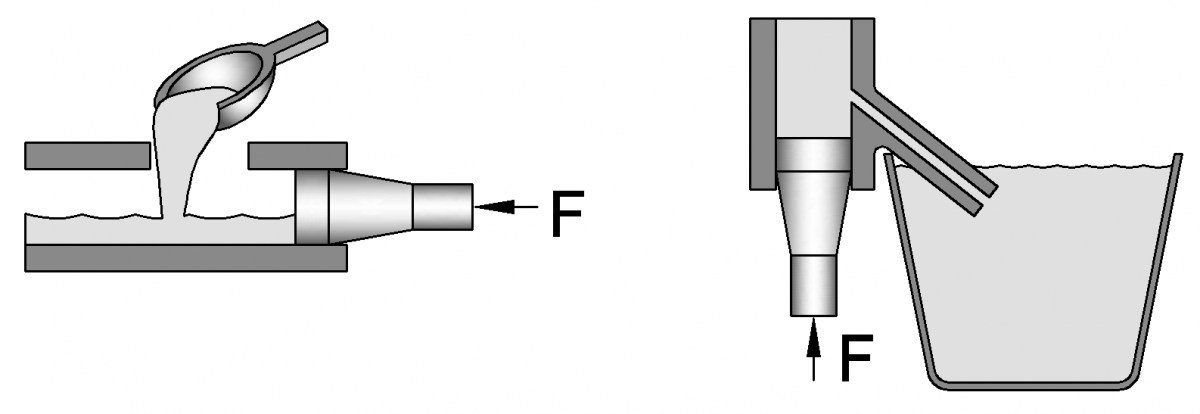
Both hot chamber and cold chamber die casting machines have their own unique advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of which type of machine to use will depend on the specific requirements of the part being produced. Factors such as the melting point of the metal, the size and complexity of the part, and the desired production rate will all play a role in determining which type of machine is best suited for a given application.
