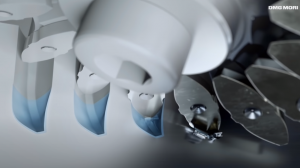
Gear manufacturing is the process of creating gears, which are important components in many machines and mechanisms. There are several methods used in gear manufacturing, including hobbing, shaping, skiving, milling, broaching, and grinding. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of method depends on the type of gear, its size, material, and required accuracy.
Hobbing is a widely used gear manufacturing method, especially for larger gears. It involves using a hob cutter to create the teeth of the gear, which rotates against a blank workpiece. The hob cutter has a series of teeth that progressively cut the gear teeth into the blank workpiece. Hobbing is a fast and efficient process that can create accurate gears with a good surface finish.
Shaping is another method used in gear manufacturing, and it involves using a shaping cutter to cut the teeth of the gear into a blank workpiece. The cutter moves in a reciprocating motion to cut the gear teeth, and the gear rotates to ensure that the teeth are cut to the correct depth. Shaping is typically used for smaller gears and is a slower process than hobbing.
Skiving is a method used for creating high-precision gears. It involves using a skiving cutter to remove material from the gear blank at a specific angle, creating the gear teeth. Skiving can create gears with high accuracy, excellent surface finish, and reduced noise and vibration. This method is often used for high-performance gears in applications such as automotive transmissions.
Milling is another method used in gear manufacturing, and it involves using a milling cutter to create the gear teeth. The cutter (generally an involute cutter) is rotated against the gear blank, and the gear blank is fed into the cutter to create the teeth. Milling can be used for a wide range of gear sizes and can create gears with complex shapes and profiles.
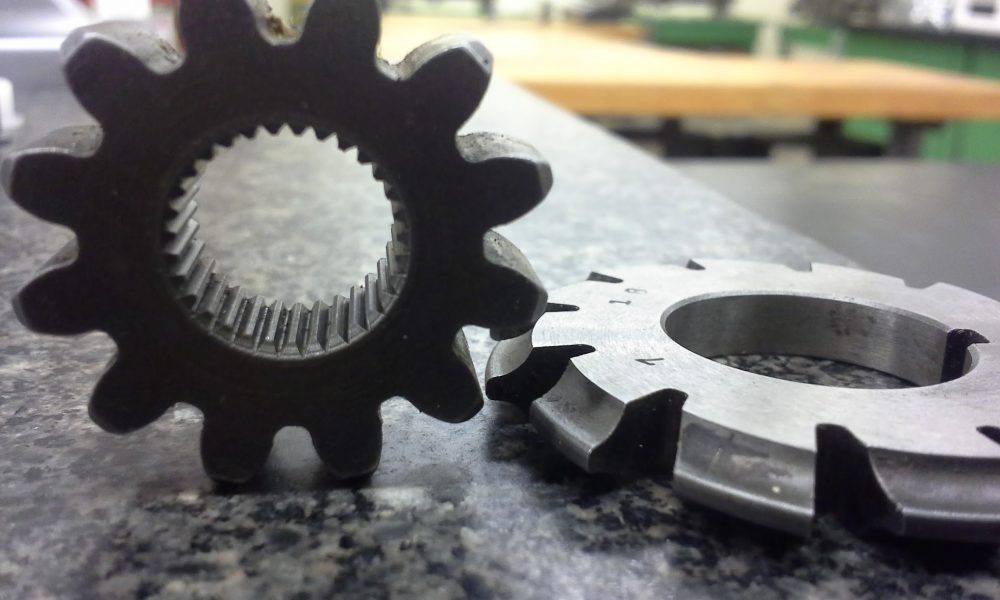

Broaching is a method used to create internal gears, splines, and other internal shapes. It involves using a broaching tool that has teeth in a specific pattern to remove material from the gear blank. Broaching is a precise process that can create accurate and repeatable internal shapes, but it is typically slower than other methods.
Powder metallurgy is another method for manufacturing gears. In this process, metal powder is compressed into the desired shape and then heated to fuse the particles together, forming a solid part. This technique offers several advantages, including the ability to create complex shapes and high production rates. Powder metallurgy also produces parts with a uniform density and excellent dimensional accuracy. However, as it requires hard tooling, it can be more expensive than other manufacturing methods. Powder metallurgy is particularly well-suited for producing small, intricate gears with high precision requirements, such as those used in medical devices or aerospace applications.
Finally, grinding is a method used for finishing gears after they have been machined. It involves using a grinding wheel to remove small amounts of material from the gear teeth to improve their surface finish and accuracy. Grinding can be used to create very precise gears, but it is a slower process than other methods.