Machine elements and features are the building blocks of machines, and they include a wide variety of components, such as gears, bearings, shafts, springs, couplings, and many others. These elements are designed to perform specific functions within a machine, such as transmitting power, providing support, controlling motion, and absorbing shock and vibration. Machine elements and features are typically designed to be durable, reliable, and efficient, and they are often subject to rigorous performance requirements. Understanding the properties, design, and selection of machine elements and features is essential for designing and building machines that can meet the demands of modern industry.
Machine Elements & Features
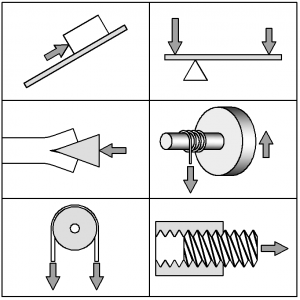
- Simple Machines
- Lever
- Inclined Plane
- Wheel and Axle
- Pulley
- Wedge
- Screw
- Fluid Conveying, Control and Actuation [See Fluid Power Components]
- Fluid Power Components
- Industrial Gas
- Plumbing, Fittings, Pipe, Tubing. See also metal shapes
- Actuators
- Valves
- Tension Members
- Cable and Rope
- Thimbles, etc.
- Rails, Ways, DIN rail, Unistrut
- See also, metal shapes
- Thompson Rod
- Mounted Rod Rails
- Ball Spline Linear Shaft
- Bearings
- Compression Members and Rods
- See also: Axles, Shafts, Spindles and Arbors
- Pitman, Connecting Rods
- Push Rods
- Control Rods
- Axles, Shafts, Spindles and Arbors
- See also: Rods, Rails, Round Bar
- Keys, Keyways and Keyseats
- Splines
- Ratchets
- Cams and Cranks
- Crankshaft
- Swashplate
- Geneva Mechanism
- Intermittent Gearing
- Clutches & Intermittent Drives
- Overrunning Clutch, See also: Ratchets
- Couplings and Clutches
- Detent (also linear)
- Hirth Joint
- Universal Joint
- Heim Joint
- See also: Ratchets
- Overrunning Clutch
- Machine Tapers and Collets
- Machine Tapers
- Collets
- Wheels and Tires, Rolls
- Seals and Gaskets
- O-Rings
- Hinges and Pivot Joints
- Ball Pivot
- Cogs, Gears and Sprockets
- Involute Development
- Planetary Gears
- Design of Spur Gears
- Racks
- Worm Gears
- Sprockets
- Roller Chain
- Timing Pulleys & Belts
- Harmonic Drive
- See also: Ratchets
- Springs
- Compression
- Tension
- Conical
- Torsion
- Wave Disk
- Linear Wave
- Strip, Constant-Force
- Fasteners
- See also, screw threads
- See also, Adhesives & Sealants
- Integral fasteners
- Permanent or Nonpermanent Categories
- Tabs
- Boss (staking)
- Fits – Press fit, shrink fit
- Keder Rail
- Crimp (see ferrule)
- Swage
- Bead, roll
- Sheet metal seams
- Snap Fit Connections
- Discrete Fasteners
- Threaded
- Bolts
- Screws
- Nuts
- Inserts
- Non-Threaded
- Pints
- Retaining Rings
- Nails
- Rivets
- Ferrules
- Threaded
- Actuators, Levers, Handwheels
- Design Features
- Draft Angle
- Boss
- Grooves and Glands
- Knurls
- Keyways & Keyseats
- Screw Thread
- Fillets & Rounds
- Chamfer
- Taper
- Gusset
- Hole Features
- Countersink
- Counterbore
- Counterdrill
- Spotface
Separately
Kinematics, Dynamics
References
Mott, Robert L, et al. Machine Elements in Mechanical Design. New York, Pearson, 2018.