- Pattern: A replica of the desired part, used to create the mold.
- Mold: A cavity created by packing sand around the pattern.
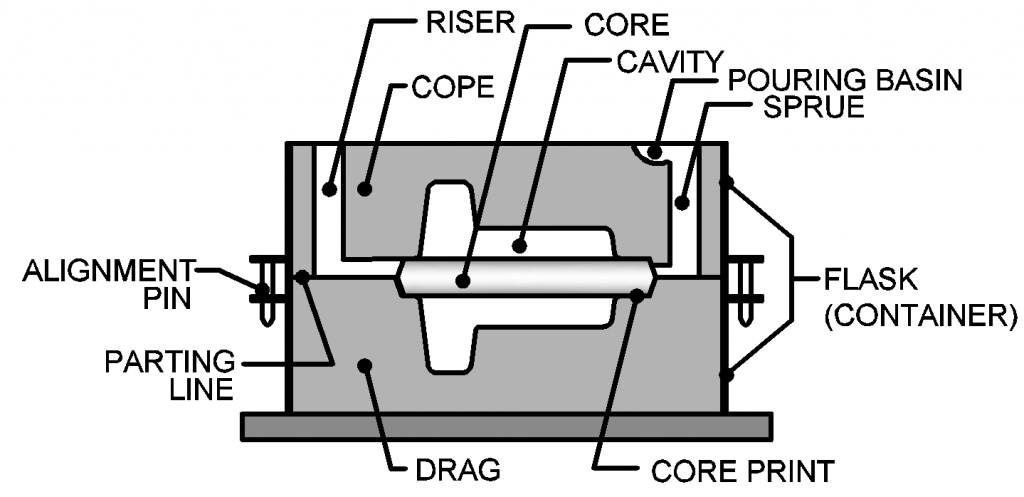
- Core: An insert placed in the mold to produce internal features of the part.
- Riser: A reservoir of metal that provides feed to the part as it solidifies, ensuring that the part solidifies from the inside out.
- Gating system: A series of channels that direct the flow of metal into the mold.
- Pouring basin: The area where the liquid metal is poured into the mold.
- Sprue: The main channel that directs the flow of metal into the mold.
- Runner: A secondary channel that directs the flow of metal to the individual cavities in the mold.
- Flask: A metal frame that holds the mold during casting.
- Chill: A metal insert placed in the mold to rapidly cool a specific area, which improves the mechanical properties of the part.
- Shrinkage cavity: An opening in the mold that allows for the contraction of the metal as it solidifies.
- Risering: The process of adding metal to the mold to compensate for the shrinkage that occurs as the metal solidifies.
- Knockout: The process of removing the part from the mold after casting.
- Deburring: The process of removing any rough edges or excess material from the cast part.
- Finishing: The process of smoothing and refining the surface of the cast part.
- Cope: The upper half of the mold, which forms the top surface of the part.
- Drag: The lower half of the mold, which forms the bottom surface of the part.
- Parting line: The line that separates the cope and drag sections of the mold.
- Cavity: The interior space of the mold, which determines the shape of the final cast part.
- Draft: The taper provided on the sides of the mold to facilitate removal of the pattern and to ease the release of the part from the mold.


