Engineering Design Graphics

Expanded Outline
I. Introduction to Engineering Graphics
A. Overview of Engineering Graphics in Engineering Technology
B. Importance of Working Drawings in Engineering Technology
C. Purpose of Working Drawings
D. Overview of Engineering Drawing Conventions and Standards
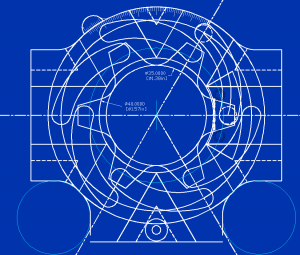
II. Blueprint Reading
A. Understanding Blueprint Reading Fundamentals
B. Types of Engineering Drawings
C. Blueprint Reading Techniques and Best Practices
III. Scales and Units of Measurement
A. Introduction to Scales and Units of Measurement
B. Common Units of Measurement for Engineering Drawings
C. Use of Scales in Engineering Drawings
D. Scaling Techniques for Accurate Measurements
IV. Drawing Instruments
A. Overview of Common Drawing Instruments
B. Use of Drawing Instruments in Engineering Drawings
C. Best Practices for Care and Maintenance of Drawing Instruments
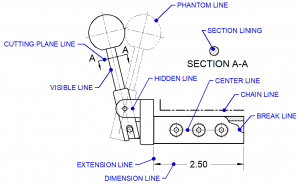
V. Alphabet of Lines
A. Introduction to the Alphabet of Lines
B. Types of Line Conventions Used in Engineering Drawings
C. Use of the Alphabet of Lines in Working Drawings
VI. Lettering
A. Introduction to Lettering in Engineering Drawings
B. Types of Lettering Styles Used in Engineering Drawings
C. Best Practices for Lettering in Working Drawings
VII. Geometry Review
A. Overview of Basic Geometric Concepts
B. Types of Polygons, Circles, and Curves
C. Use of Geometry in Engineering Drawings
VIII. Geometric Construction
A. Introduction to Geometric Constructions
B. Types of Geometric Constructions Used in Engineering Drawings
C. Geometric Construction Techniques for Engineering Drawings
D. Best Practices for Geometric Construction in Working Drawings
IX. Orthographic Projection
A. Introduction to Orthographic Projection
B. Types of Orthographic Projections Used in Engineering Drawings
C. Orthographic Projection Techniques and Best Practices
D. Applications of Orthographic Projection in Working Drawings
X. Standard Views
A. Overview of Standard Views in Engineering Drawings
B. Types of Standard Views Used in Working Drawings
C. Best Practices for Producing Standard Views in Engineering Drawings
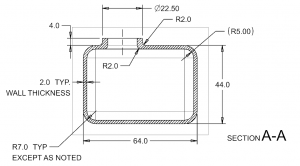
XI. Section Views
A. Overview of Section Views in Engineering Drawings
B. Types of Section Views Used in Working Drawings
C. Best Practices for Producing Section Views in Engineering Drawings
XII. Auxiliary Views
A. Introduction to Auxiliary Views in Engineering Drawings
B. Types of Auxiliary Views Used in Working Drawings
C. Best Practices for Producing Auxiliary Views in Engineering Drawings
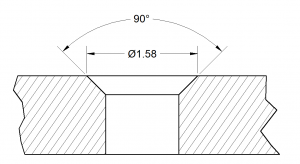
XIII. Dimensioning
A. Overview of Dimensioning in Engineering Drawings
B. Types of Dimensioning Used in Working Drawings
C. Dimensioning Techniques and Best Practices for Engineering Drawings
D. Use of Dimensioning in Orthographic Projections and Section Views
XIV. Material Specifications
A. Introduction to Material Specifications in Engineering Drawings
B. Types of Material Specifications Used in Working Drawings
C. Best Practices for Incorporating Material Specifications in Engineering Drawings
XV. Pictorial Views
A. Overview of Pictorial Views in Engineering Drawings
B. Types of Pictorial Views Used in Working Drawings
C. Best Practices for Producing Pictorial Views in Engineering Drawings
XVI. Descriptive Geometry
A. Introduction to Descriptive Geometry
B. Orthographic Projections
C. Intersections of Planes and Solids
D. Development of Surfaces
E. Applications of Descriptive Geometry in Working Drawings
XVII. Contour Maps
A. Cut and Fill
B. Strike and Dip
C. Outcrop and Dip Direction