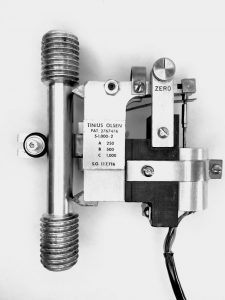
Mechanical properties are a fundamental aspect of engineering materials that play a critical role in determining their suitability for specific applications. Mechanical properties refer to the physical characteristics of materials that describe how they respond to external forces, such as tension, compression, bending, or twisting. These properties include strength, hardness, ductility, toughness, and fatigue, among...

Metals are one of the most important and commonly used types of engineering materials. They have a wide range of physical and mechanical properties, such as high strength, ductility, thermal and electrical conductivity. Some metals also provide resistance to corrosion. Due to their unique combination of properties, metals are widely used in a variety of...

Industrial gases are a crucial component in many industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, and research. These gases are used in a wide range of applications, from welding and metal fabrication to medical procedures and scientific experiments. Industrial gases are typically produced through various methods, including air separation, chemical reactions, and purification techniques. Some of the most...

Polymers are a class of engineering materials that are widely used in a variety of applications due to their unique properties and versatility. A polymer is a large molecule made up of many smaller subunits, called monomers, that are chemically bonded together in a repeating pattern. These repeating patterns give polymers their unique mechanical, thermal,...
Ceramics are a diverse category of engineering materials with a wide range of technical applications. Derived from the Greek word "keramos," meaning pottery or clay, ceramics encompass a wide range of inorganic, non-metallic materials characterized by their exceptional hardness, high melting points, and often remarkable resistance to heat, corrosion, and wear. These unique properties make...

Wood can be classified as an engineering material due to its unique combination of mechanical, physical, and chemical properties. As an organic material, wood is renewable and biodegradable, making it an attractive choice for sustainable engineering applications. Wood has a high strength-to-weight ratio, making it a lightweight yet strong material for construction and other applications....

This classification encompasses all the substances and materials used in engineering applications related to fluid mechanics, lubrication, and metalworking processes. It covers various types of fluids, including fuels, lubricants, coolants, hydraulic fluids, and metalworking fluids, all of which are essential for the smooth functioning and efficiency of machinery and engineering processes. Understanding the properties, applications,...
ASTM International, formerly known as the American Society for Testing and Materials, is a globally recognized organization that develops and publishes voluntary consensus technical standards for a wide range of materials, products, systems, and services. ASTM standards are used by industries worldwide to establish specifications and guidelines for the design, manufacturing, testing, and certification of...
Combinations of Materials Composites Dispersed Media Foams Solid Foams Open Cell Closed Cell Syntactic Foams Metal Foams Nano Foams Polymeric Foams Self-Skinning Foams Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) Extruded Polystyrene (XPS) Low Density Polyethylene (LDPE) PVC Polyurethane Polyethylene Polypropylene Silicone Nitrile Neoprene Latex foam (Dunlop Foam) Sandwich Structures Corrugated Core Honeycomb Structural Shapes...
Mechanical properties are a fundamental aspect of engineering materials that play a critical role in...
Metals are one of the most important and commonly used types of engineering materials. They have a wide...
Ferrous metals are a category of metals that contain iron as their main constituent element. The most...
Steel is a widely used alloy of iron and carbon, with carbon content typically ranging from 0.2% to...
Stainless steel is a versatile material known for its corrosion resistance, high strength, and aesthetic...
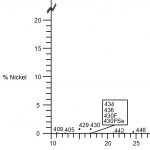
This group is the most common type of stainless steel and contains high levels of chromium (usually...
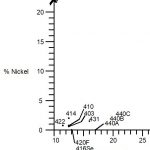
Ferritic stainless steels have little to no nickel. They are magnetic and offer good corrosion resistance,...
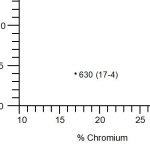
Martensitic stainless steels have a moderate chromium content (usually 12-18%) and low nickel. They...
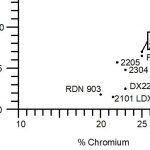
Duplex stainless steels combine the properties of both austenitic and ferritic stainless steels. They...
Precipitation-hardening stainless steels contain chromium, nickel, and other alloying elements such...