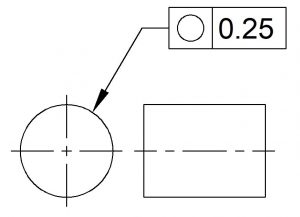
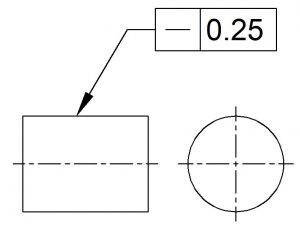
Form tolerances limit the amount of deviation from a perfect geometric form, such as a line, circle, plane or cylinder. They control only features themselves, and not in relation to any other feature.
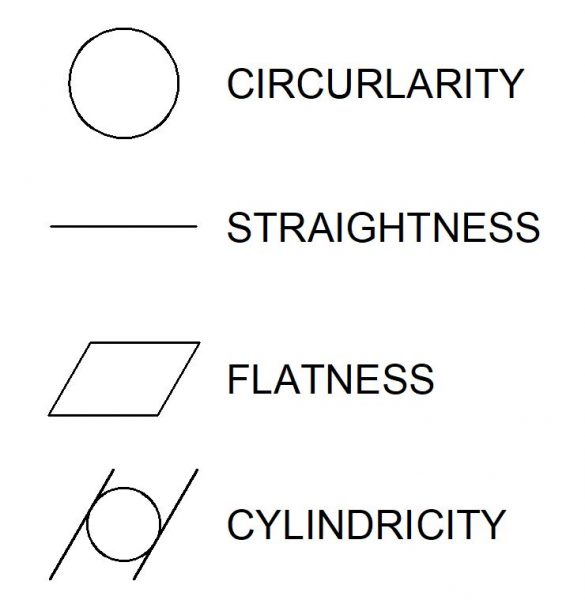
Form tolerances limit the amount of deviation from a perfect geometric form, such as a line, circle, plane or cylinder. They control only features themselves, and not in relation to any other feature.