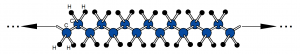
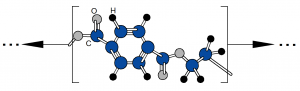
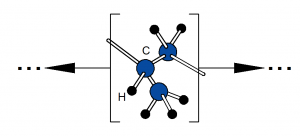
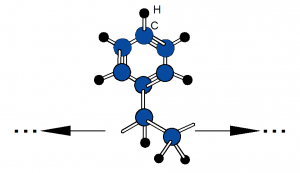
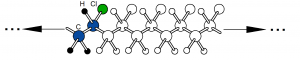
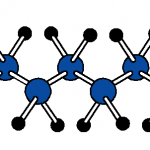
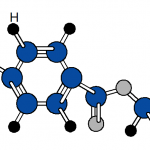
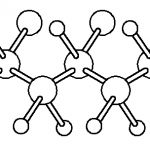
Thermoplastics are a class of polymers that soften when heated and harden upon cooling, without undergoing significant chemical change. This behavior is primarily associated with linear or lightly branched molecular structures in which polymer chains are held together by secondary intermolecular forces rather than extensive covalent crosslinking. When heat is applied, these intermolecular forces are reduced, allowing the chains to move past one another and the material to be reshaped. Upon cooling, the forces are re-established, and the material returns to a rigid or semi-rigid state. This reversible thermal behavior distinguishes thermoplastics from thermosetting polymers, which form permanent crosslinked networks during curing and cannot be remelted.

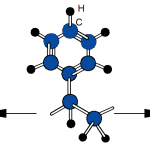
From a materials engineering perspective, thermoplastics are characterized by their glass transition temperature (Tg) and, for semi-crystalline polymers, their melting temperature (Tm). Below Tg, amorphous thermoplastics behave as rigid, glass-like solids; above Tg, they exhibit increased ductility and toughness. Semi-crystalline thermoplastics contain both amorphous and ordered crystalline regions, leading to distinct melting behavior and often higher strength and chemical resistance. The balance between amorphous and crystalline structure, along with molecular weight and chain architecture, strongly influences mechanical properties, processing temperatures, and dimensional stability.
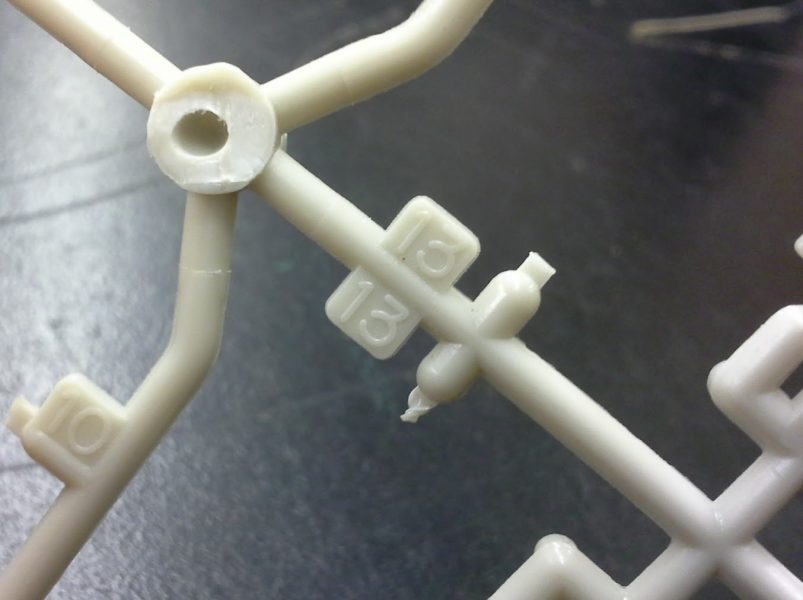
Thermoplastics are widely used in manufacturing because they can be repeatedly heated, formed, and cooled using processes such as injection molding, extrusion, thermoforming, and blow molding. Common examples include polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polystyrene (PS), and polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Their reprocessability, relatively low processing temperatures compared to metals, and compatibility with high-volume production methods make thermoplastics essential materials in modern engineering technology applications, ranging from packaging and consumer products to automotive components and electrical insulation.