Petroleum, commonly known as crude oil, is a complex and naturally occurring fossil fuel formed over millions of years from the remains of ancient marine organisms. Composed mainly of hydrocarbons, which are organic compounds containing hydrogen and carbon, petroleum plays a crucial role as a source of energy and raw material for a diverse range...

Coatings refer to thin layers of material applied to the surface of a substrate or component for various functional purposes. These coatings serve a range of purposes, and their application can significantly enhance the performance, durability, and appearance of the underlying material. Here are some key aspects of coatings from an engineering perspective:
When mixing solutions, paints, or cleaners, we often use mix ratios to describe how much of one substance is combined with another. Understanding how to convert a mix ratio into a percent concentration is important for preparing mixtures accurately and safely. What Percent Concentration Means Percent concentration tells us how much of the total mixture...
In many industrial and laboratory settings, you may need to adjust the concentration of a liquid mixture to meet specific requirements. This commonly happens with coolants, cleaning solutions, plating baths, or any process where a solute (like a concentrated chemical) is mixed with a solvent (usually water). The basic approach is to calculate how much...
Petroleum, commonly known as crude oil, is a complex and naturally occurring fossil fuel formed over...
SAE J300. This standard, titled "Engine Oil Viscosity Classification," outlines the classification system...
Gasoline, often referred to as petrol, is a liquid fuel derived from petroleum through the refining...
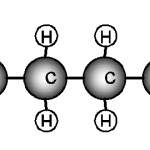
Octane is a hydrocarbon molecule, specifically an alkane with the chemical formula C8H18. It is a colorless...
Coatings refer to thin layers of material applied to the surface of a substrate or component for various...
When mixing solutions, paints, or cleaners, we often use mix ratios to describe how much of one substance...
In many industrial and laboratory settings, you may need to adjust the concentration of a liquid mixture...